February 2023 Consumer Sentiment Index | Published: 24/02/23
Consumer confidence continues on a cautious but positive path
Section I; Broadly steady February sentiment reading hints at underlying improvement
Irish consumer sentiment rose fractionally in February, the fourth improvement in the Credit Union Consumer Sentiment Index in the past five months. The modestly improving trend in confidence of late hints that we may have moved past ‘peak fear’ in relation to consumers concerns around cost-of-living pressures and the threat of markedly weaker economic conditions.
However, the February reading also suggests that while concerns may be easing, there is absolutely no sense that they have ended. The sentiment survey clearly signals that Irish consumers remain cautious and constrained in their spending power. So, the February data suggest that a significant fear factor remains a key influence on Irish consumer sentiment.
While we previously suggested the sentiment survey was signalling an element of resilience through last year that hinted Irish consumers were down but not out, we would interpret recent readings as suggesting consumers feel their concerns may be easing but far from over.
The slight increase in consumer confidence in February suggests no major change in consumer thinking this month. As the sentiment index has fallen in February in 18 of the previous 26 years, likely reflecting post-Christmas bills and dark and cold weather, the marginal pick-up in confidence this month may hint at an underlying improvement that likely comes from some modest easing in concerns around cost-of-living pressures.
This may be due in part to relatively mild and dry weather through the survey period that should translate into lower than feared heating bills. The ongoing easing in wholesale energy costs should also have helped through the prospect of less threatening utility bills in the months ahead. Finally, the continuing health of economic indicators such as exchequer returns and unemployment data through the survey period may have lessened nervousness that a marked slowdown was inevitable and possibly underway.
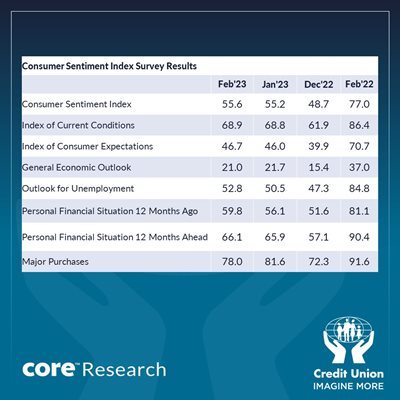
As the table above indicates, the Credit Union Consumer Sentiment Index rose to 55.6 in February from 55.2 in January. An increase of this magnitude does not suggest any material change in the mood of Irish consumers this month.
The February 2023 reading is well below that of a year ago when the index stood at 77.0 just before the Russian attack on Ukraine. This reflects the draining impact of that shock on the cash and confidence of Irish consumers.
However, the February result is the strongest since June 2022 and, as such, shows a continued gradual recovery in sentiment from the exceptionally weak readings that followed Russia’s invasion of Ukraine as the Irish economy has again proven resilient and the worst fears that emerged a year ago have not been realised.
The increase In Irish consumer sentiment in February mirrored gains in similar confidence measures for the US and the EU. This hints at the role played by easing energy costs globally as well as a modest pullback in inflation rates. That said, consumer confidence globally remains quite subdued as pressures on household finances remain substantial and recession fears persist.
The marginal improvement in the Credit Union Irish Consumer Sentiment Index in February was the result of offsetting movements in the five key components of the survey, with three recording month-on-month gains and two posting declines.
Irish consumer thinking on the 12-month economic outlook weakened slightly in February, a slightly surprising result given generally positive news-flow through the survey period. However, this element has seen a marked recovery of late and, with continuing nervousness around the multinational sector and major difficulties in the housing market, it may be that consumers continue to feel very cautious about macro prospects.
In contrast, sentiment in relation to jobs improved for the third month in a row in February. Relatively positive commentaries from recruitment firms on job prospects for the coming year coupled with widespread reports of job vacancies were underpinned by official data showing the job growth continued in December while the unemployment rate remained at 4.4% in January. As a result, the concerns that emerged through the autumn on tech sector layoff announcements have eased considerably.
As an aside, the recent fluctuations in the jobs element of the survey coupled with this week’s Labour force Survey data showing sustained strong growth in employment in the final quarter of 2022 emphasise the significant ‘real’ impact of developments in the multinational sector on the Irish economy.
In turn, this suggests that although some growth metrics may not fully reflect the economic conditions being felt by most households and firms, the importance of multinational employment means that ‘leprechaun’ economics is far more than a fairy-tale. Indeed, Irish jobs growth was more than two and a half times faster than in the rest of the Euro area in 2022. If the Euro area had posted the same rate of jobs growth as Ireland, GDP growth for the Euro area might have reached 8% last year, a near leprechaun rate!
The most notable improvement between January and February sentiment readings was seen in consumers assessment of the change in their household financial circumstances through the past twelve months. At the margin, an easing in official inflation figures may have helped in this regard but with an overall inflation rate of 7.8% in January and double digit increases in high profile areas such as food (+12.8%) and energy (+33%), the financial circumstances of many Irish households remain strained.
We would also note that the drain on household purchasing power from higher inflation in 2022 was much greater than that suggested in commentary on this week's Survey of Income and Living Conditions (SILC) data from the CSO. As the CSO use previous year income and inflation data in their analysis, this means the inflation hit in the SILC report reflects 2021's 2.4% rise in consumer prices rather than the 7.8% increase in 2022. As a result, the true inflation hit to the average Irish household in 2022 is broadly in line with our previous estimate at around €3,500 rather than the widely reported €1,000 figure.
Our sense is that the key driver of the more positive reading in this element of the sentiment survey is that most consumers had braced themselves for even more severe cost-living pressures in early 2023. In these circumstances, the easing in pump prices and wholesale energy costs more generally encouraged the view that the worst may be over in this regard, but mild weather likely also played an influential role by limiting heating usage.
The sense that sentiment has been boosted by a sense that that the conditions consumers are facing are not as bad as feared rather than materially improved is consistent with altogether more cautious readings in the February survey in regard to households expectations for their spending power over the next twelve months-which increased only marginally in February, and, more tellingly, by a significant pullback in spending plans which was the weakest element of the survey in February.
If consumers were signalling a clear improvement in their current financial conditions, we might expect a more upbeat assessment of the buying climate at present. So, the broad message of the Credit Union Consumer Sentiment survey for February would appear to be that concerns are easing but they are far from over. As a result, the mood of Irish consumers is still cautious.
Section II
Could improving confidence lead to stronger consumer spending through a run-down in savings?
While theory might suggest that consumers would build up savings during economic ‘good times’ and draw them down when facing difficulties, much of the evidence from Ireland and elsewhere suggests that households tend to save more during more difficult or uncertain times and run these down when consumers become more optimistic and ‘animal spirits’ take hold. This holds out the possibility that improving consumer sentiment in 2023 could unlock some pandemic savings and boost consumer spending.
Although the ‘lockdown’ element of the pandemic prompted a build-up of forced savings in Ireland and other countries, official data suggest the that in the third quarter of 2022, the savings rate of Irish households was well down from the Quarter2 2022 pandemic peak of 33.8% but still exceptionally elevated at 19%-the pre-Covid norm was around 10%. In broad terms, this figure might appear consistent with the caution evident in the corresponding consumer sentiment data but it also seems a touch high given the indications of widespread financial strains in the sentiment survey.
The February 2023 sentiment survey contained a special question examining the uses to which additional pandemic savings built up during the pandemic were put. The responses shown in the table below suggests that the rundown of savings is unlikely to give a dramatic boost to consumer spending in the near term, but it could give extra impetus to an eventual upturn.
As the table indicates, about 50% of Irish consumers saved more during the pandemic. 15% of all consumers have spent those savings in the interim. Some of this group may have used those savings as a buffer against cost-of-living pressures. A further 10% of all consumers have set these extra savings funds aside for a specific long-term purpose such as home improvements or education costs.
Some 25% of Irish consumers say they have built up additional savings for ‘rainy day’ purposes. This reflects a still pervasive 'fear factor' on the part of Irish consumers. Some element of this additional ‘savings’ is likely to be in the form of debt reduction such as cutting amounts owed on overdrafts or credit cards. However, much of it is likely seen in a build-up of cash savings in the banking system.
Central Bank data show that, in the year to December2022, household deposits rose at a slower pace than prior to the pandemic, an outturn consistent with these survey results. Drawing on the same Central Bank data set, we estimate that household deposits are now approximately €15 billion higher now than they would be if the pre-pandemic trend in deposit growth had persisted.
Although savings held for specific purposes will eventually find their way into the economy, this is likely to happen in a phased manner. However, an easing in the current 'fear factor' and an allied sharp improvement in consumer sentiment might see some winding down of those savings held on a ‘precautionary’ basis.
On the admittedly strong assumption that savings are evenly distributed across households, we think a gradual release of a significant element of such savings might see between €5 and €10 billion percolate through the Irish economy on a marked pick-up in consumer confidence.
While current cost of living pressures suggest continued caution in sentiment and downside risks to consumer spending are likely to persist in the short term, these results hint at a tilt towards upside risks when such constraints eventually ease.
The Credit Union Consumer Sentiment Survey is a monthly survey of a nationally representative sample of 1,000 adults. Since May 2019, Core Research have undertaken the survey administration and data collection for the survey. The survey was live between the 3rd and 20th February 2023.